
Course code cyber analysis (Secure code review)
A Course code cyber analysis also know as a secure code review is a specialized process that involves manually and/or automatically reviewing an application's source code in order to find security-related problems. A secure code review does not strive to find every flaw in the code; rather, it seeks to provide insight into the sorts of vulnerabilities that exist and to assist the application's developers in understanding what issues are present. The purpose is to provide developers with information that will aid them in making the source code of the application more sound and safe.
A secure code review concentrates on seven different security techniques or regions. An application that is vulnerable in any way makes it a target for a hostile user and raises the chances of it being used in an attack. A secure code review should educate developers about the source code's soundness in each of the following areas:
- Authentication
- Authorization
- Session management
- Data validation
- Error handling
- Logging
- Encryption
Manual vs. Automated Review
A secure code review can be either manual or automated, each with its own set of benefits and drawbacks. An analyst performs a manual review by going through the code line by line, looking for errors and security issues. A tool is used to scan the code and flag potential issues in an automated review.
Manual review takes time and requires significant domain expertise to complete correctly. Manual code review can often take years of practice to become efficient. Errors in the review (missed and incorrect findings) are unavoidable even with experienced human analysis. According to the MITRE Secure Code Review Practice, a skilled reviewer can complete approximately 3,000 lines of code per day.
Automated review aids in the resolution of issues associated with manual review. Good automated review tools, on the other hand, are not cheap. Furthermore, the technology underlying automated tools is only effective at detecting certain types of flaws. A single automated tool may be effective at detecting some issues but ineffective at detecting others. Using multiple automated tools can help to mitigate this issue, but it will still not uncover every issue. Automated tools also have a tendency to generate false positives (reported findings that are not actually issues). Adjudicating false positives necessitates human intervention and depletes the development team's time.
Prevention is better than to cure, and this also applies to software development, which is why it is critical to look for vulnerabilities early in the development process. There are already several plugins in Ide that scan your code on a regular basis. This reduces the client's vulnerability to vulnerabilities. But again, your software and you may overlook something.
Manual
Over-the-Shoulder Code Reviews
Over-the-shoulder code reviews take place at the developer's workstation, where an experienced team member walks through the new code and offers ideas in the form of a dialogue. It is the simplest method for conducting code reviews and does not necessitate a pre-defined structure.
In addition to any official code review procedure that may be in place, such a code review may still be done informally today. Over-the-shoulder code reviews have typically been done in person, but distant teams can use collaborative tools to do so as well.
Pair Programming
Pair programming is a process of continuous code review. Two developers are seated at a workstation, but only one is actively coding, while the other provides real-time feedback.
While it may be a useful tool for inspecting new code and training developers, its time-consuming nature may make it inefficient. During the review period, the reviewer is prevented from doing any other productive work.
Digital
If you use GitHub to maintain your Git repositories on the cloud, you may have already used forks and pull requests to review code. In its pull requests, GitHub includes a code review tool. The code review tool is included in GitHub's core service.
A reviewer who has access to the code repository on GitHub can assign themselves to the pull request and complete a review. A developer who has submitted a pull request may also request that an administrator review it.
Automation
Automated code review tools have been around for a while as static analysis and unit testing frameworks. However, because business needs necessitate speed and agility, code review must be automated. It can result in faster feedback, higher code quality, and shorter time to production.
Can automated code reviews replace manual code reviews?
No. Manual code reviews reduce risky high level decisions such as the use of suboptimal architectures. They also support a collaborative culture and peer feedback.
While automated code reviews are better than having no code reviews, they are not a replacement for manual code reviews. However, they can make manual code reviews more efficient since they save human reviewers from looking for minor errors such as function naming, spacing or style.
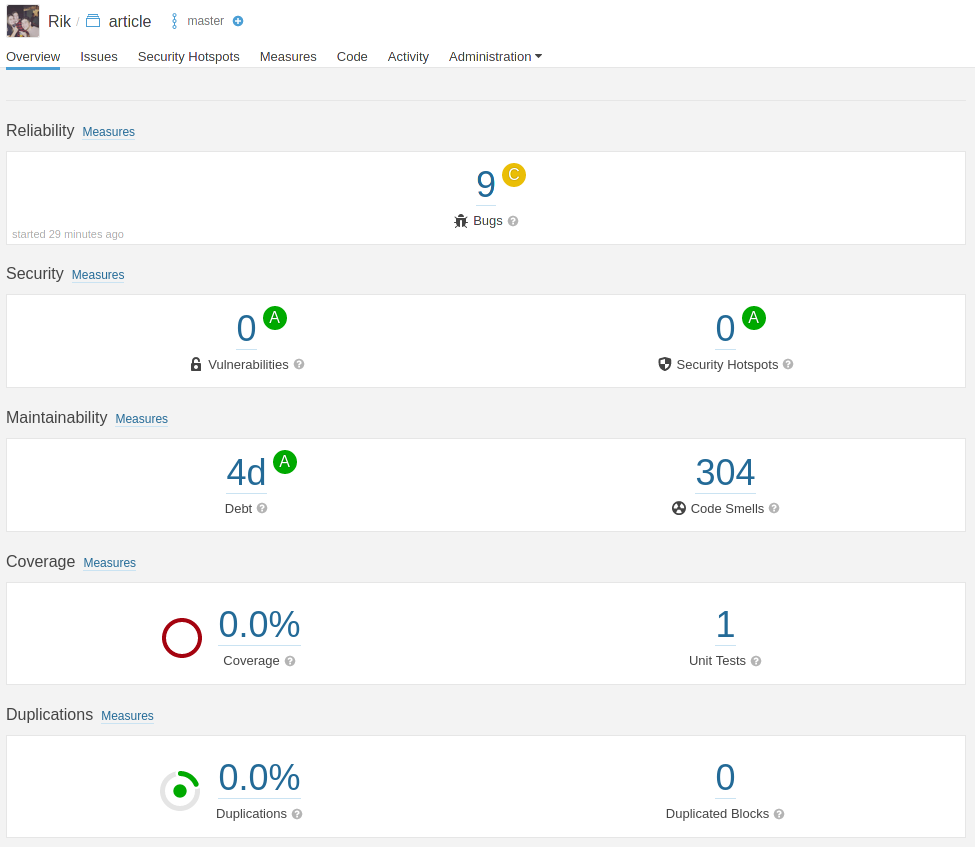
SonarQube
SonarQube (previously Sonar) is a free and open source platform for managing code quality. It is primarily a tool for developers to use in order to produce high-quality code. From a general overview of the code quality, you can navigate to the specific line(s) of code that are causing the issue. SonarQube is open source and extensible via plugins. Many programming languages are supported by the application, including Java, JavaScript, C#, C++, COBOL, PHP, and others. These languages can be examined for quality issues such as code duplication, test failures, and a variety of other issues. I'll go over some of the new and unknown features in this article.
Implementation
In my sixth semester, I also used sonarqube to ensure my code quality. As described above, prevention is better than to cure so I have installed the sonarqube plugin inside my IDE which checks every time I save my file to see if there are things that need to be adjusted. I also implemented sonarqube within my CI/CD module which when I made a commit to my repository automatically tested my code. If it then failed, my code was not uploaded within my github repo.
I chose this solution because automated solutions can be quite expensive and the costs can add up quickly. The SonarQube solution is open source so it is free to use and is well maintained by the community. The analyses performed on my code are divided into several domains so is the cyber domain also one of them.
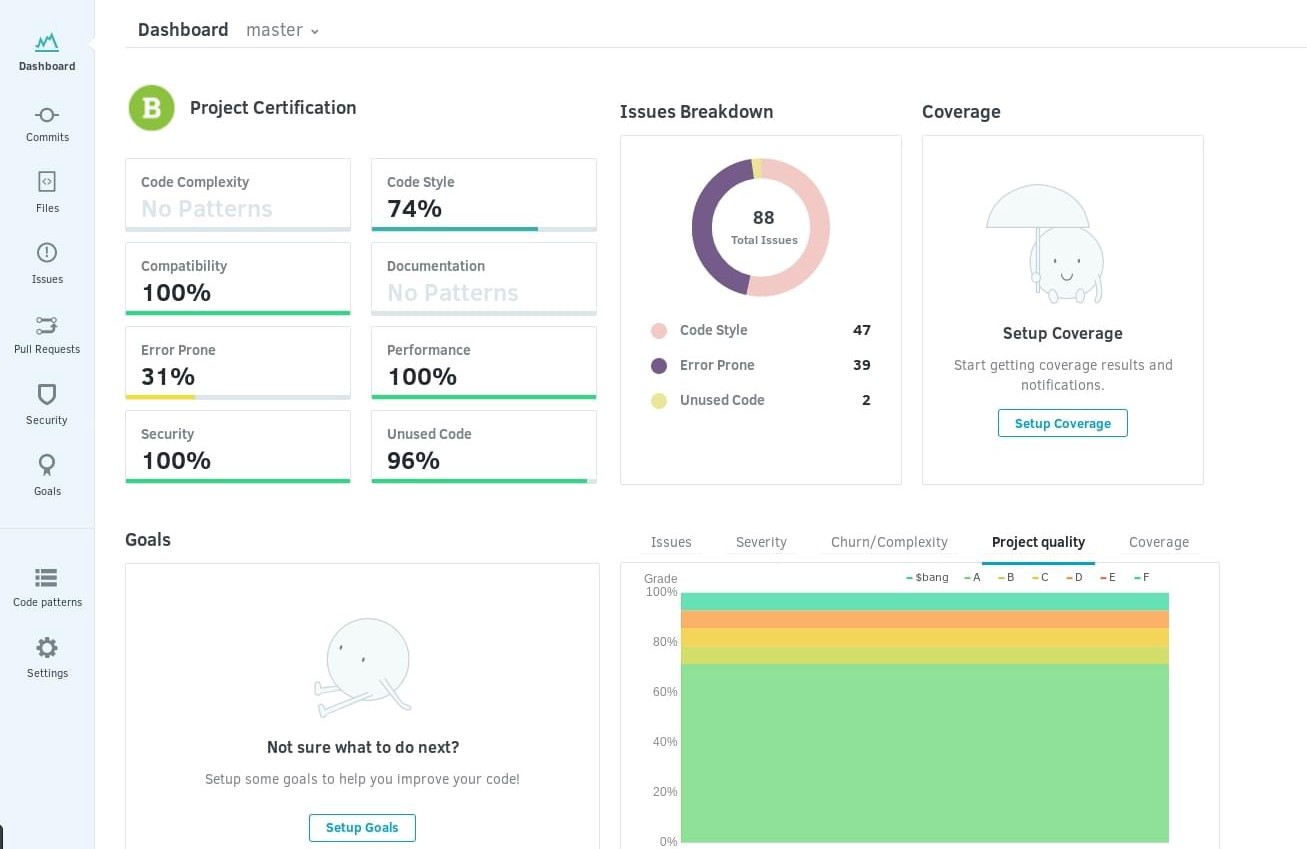
Codacy
Codacy automates code reviews and monitors code quality on every commit and pull request, reporting back on the impact of each commit or pull request, code style, best practices, security, and many other issues. It tracks changes in code coverage, duplication, and complexity. Saving developers' time during code reviews, allowing them to tackle technical debt more effectively. Currently, JavaScript, Java, Ruby, Scala, PHP, Python, CoffeeScript, and CSS are supported. Codacy is static analysis without the complication.
Sources:
Thank you for reading this topic about Course code cyber analysis I hope it was interesting any feedback is always welcome. Hope to see you in the next topic,
Byee! 👋🍺
TL;DR COurse code review with a cyber aspact